Building a Digital Marketing Strategy from A to Z
Mục Lục
- What is strategy?
- The hierarchy of a strategy
- How are strategies and tactics different?
- Why do we need a digital marketing strategy?
- The constituting elements of a good strategy
- 3 fundamental foundations of digital marketing
- 3 Steps to Prepare for Planning Your Strategy
- 1.Assessing the situation
- Building a digital marketing strategy – step by step
- 2. Estimable Factors
- Strategy: easy to say, hard to do but still have to work on
If your business uses digital channels to find and approach customers, the need to build a complete digital marketing strategy to optimize costs as well as to sustainably develop is necessary. Strategy has a great impact on results as well as business performance and all other aspects. However, there are a number of businesses that struggling with developing their own strategies. Strategy is not something that is too difficult or too complex to understand, just by understanding correctly and being acquainted with the steps, almost everyone can build the right strategy for their business.
The purpose of this article is to help readers understand the fundamentals of strategy as well as the step-by-step guide to creating a complete digital marketing strategy. And with these steps you can build almost any kind of strategy, not just digital marketing.
* Before going deep into the article, I want to say that what I write and share in the article is what I am using to build the strategy for myself. This is not the only way, and I believe that everyone can have their own way and that there may be others which are more efficient and better than mine.
What is strategy?
Strategy is a top-level plan to acquire one or many OBJECTIVES under vague conditions – Wikipedia
What you need to pay attention to in the definition above is the keyword “objective”. The essence in which a normal plan can become a strategic goal is that it must serve one or more strategic goals. What is called a strategic goal?
The strategic goal of a typical business or company will only be one of the following:
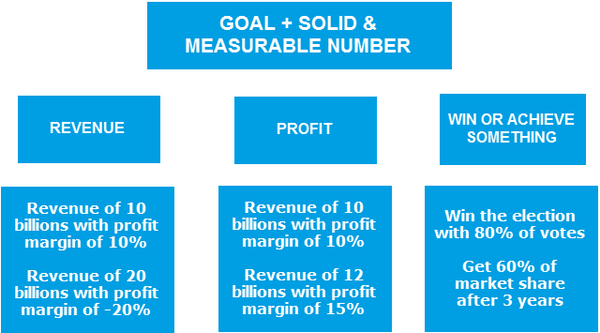
The strategy has three types of objectives: revenue, interest or achieving something.
Revenue: is the sum amount from the proceeds from the sale of products, goods or services and not deducted or excluded from other expenses.
Profit: The remaining amount of the company after deducting all other costs including the expenses of production, advertising, taxes, etc.
To achieve something: there is no need to explain.
For example, this month your sales target is $ 10 billion with a profit margin of 10%, but next month you want to increase sales by $ 20 billion by willingly sacrificing profit margins and leaving the loss up to 20% (by applying discount, voucher or promotion, etc … to stimulate the purchasing demand). To increase sales, your strategy will often have to target external factors.
An example of a strategic goal for profit: this month you have the revenue of 10 billion with the profit margin of 10%, next month the revenue just slightly increases by 2 billion but the profit margins must increase to 15% (by reducing production costs, improving workflow, saving costs, reducing marketing costs, etc., to increase the profits). To increase profits, your strategy often has to target the internal factors of the business.
An example of winning or achieving goals may be to win the election with 80% of the votes or occupy 60% market share after 3 years.
All of the three goals mentioned above are linked to a clear and measurable number (sales, profits, percentages), and each of these strategies is designed to serve Achieve a predefined goal.
We will talk more about how to set up a digital marketing strategy below.
The hierarchy of a strategy
A strategy also has several levels and each level serve a specific target. Usually, we have three levels: Corporate Strategy, Business Strategy, Functional / Operational Strategy.

Corporate Strategy: This is the strategy at the highest level that will determine what kind of business the company (or companies) will do, what is their business viewpoints and perspectives, how they distribute their finance to their lower business units (if the corporation has many companies). Because of its nature, corporate-level strategies are more about value, philosophy, and concept rather than concrete and detailed plans like Business and Operations Level strategies.
Business Strategy: A strategy at a corporate level that analyzes market factors to give directions on how to allocate resources and how to compete with competitors in the market and obtain the financial goals of the company.
Operational Strategy: Strategy at the operational level are usually divided into departments such as Marketing, Finance, Human Resources, Operations, etc. The strategy at this level will be about the development of detailed plans of activities and developmental orientations for the operating department.
Within this article we will only talk about the building of a digital marketing strategy at the Functional / Operational level.
How are strategies and tactics different?
Many people still confuse strategy and tactic or do don’t understand the difference between these two terms.
Simply put, tactics are smaller plans within the strategy that you set up to achieve a predefined strategic goal. Tactics also pursue their own goals and the attainment of these tactical goals, though not decisive, will directly affect the achievement of your ultimate strategic goals.
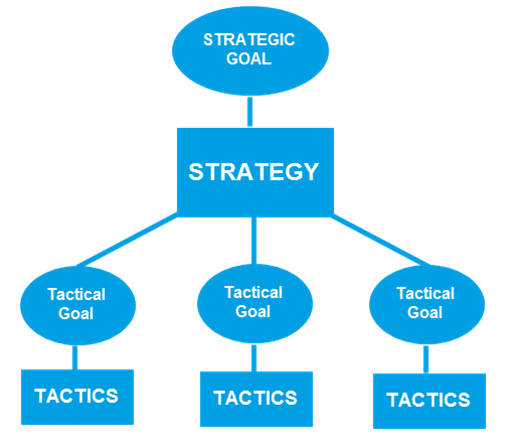
The strategy is made up of many tactics
For example, you have to build a digital marketing strategy with the goal of achieving $ 1 million a year. At this point, plans for channels such as SEO, SEM, Display, Social, etc. will be the tatics created with their own goals (how many organic traffics must be obtained from SEO, what is the number of CPA and CR of SEM and Display, how many engagements must be generated from Social, etc.).
Achieving all the tactical goals of each of the smaller channels will get you closer to achieving the final strategic objective. Failing to achieve any tactical goals does not mean that your strategy will fail, but will certainly make it harder to achieve the universal goal as the remaining channels will now have to work harder to complement the unsatisfactory channel.
Here are the basic differences of strategy and tactics in different angles:
| Strategy | Tatic | |
| Goal | Achieving a strategic goal that directly affects the survival and development of the organization. | Achieving tactical goals affects an integral part of a whole. |
| Role | Implemented by individuals who have the power to mobilize internal resources within the organization and understand how to apply a variety of tactics to achieve goals. | Specialists in a certain area have the ability to use limited resources to accomplish and achieve certain goals. |
| Responsibility | Responsible for the overall development of the organization | Responsible for a particular assigned part. |
| Duration | Long-term, often unchanged | Short-term, flexible and can change according to the market situation |
| Outcomes | Creating clear and specific goals for the organization, including plans, directions, and KPIs | Generating clear results by using manpower, tools and time |
Therefore I often avoid using words like SEO strategies, Social strategies, etc. In my opinion, those channels are just tools and plans and to effectively use these channels, we should call them tactics instead. The digital marketing strategy is at a higher level than the distribution channels (explained below in the Content section).
Also, the time to do something can not accordingly turn it into a strategy. A plan to socialize and develop a fan page for 2 years is just a tactic, same for a link building, onsite optimization campaign which lasts 3 years.
Why do we need a digital marketing strategy?
Is strategy needed? And why is it so important? Because without strategy, all we do will in the end get stuck.

Source: getty
When running ads, your CPC can only be lowered to some extent, no matter how much you optimize. Same for SEO, your traffic can not increase forever, some time Google will pull it down again. Same for any other advertising channels. All tactics will come to a standstill. Why?
If there is not a higher strategic goal to guide all tactics, you will be more likely to get caught up in the whirlwind of what you do every day. Chasing the KPIs does not make sense at all when ultimately you don’t know whether what you are doing is actually contributing to the big picture or not.
Keyword rankings this month increases over the previous month, CPC lower than 10%, Facebook page this month has an additional 5,000 likes. Oh … then what? Will this help the company to sell more? Not sure.
You can argue and say that’s what your boss or client wants. They want higher ranking keywords, lower CPCs or more page likes. They want that and you give them what they want. But why do you end up getting stuck? The boss or customers still judges that your performance is not good? The sales of the company does not increase? There must be something wrong going on here. Yes, that is the cause and also the problem, you are interested in tactics but forget about what is the strategy and its purpose. And in fact, what the boss / client wants sometimes is not necessarily the right or what really bring the benefits.
That does not mean that tactics are not good, because without them all of us are just going to be braggarts who are heading nowhere. What I mean here is that tactics need to be driven by something higher. Tactics need to work rhythmically and move towards the highest goal of the strategy.
Strategy is essential for businesses to break the law of decline mentioned above and step out of the vicious cycle to enter a bigger game.
The constituting elements of a good strategy
These are the factors and the same questions I often ask myself in order to determine whether my strategy is a good strategy:
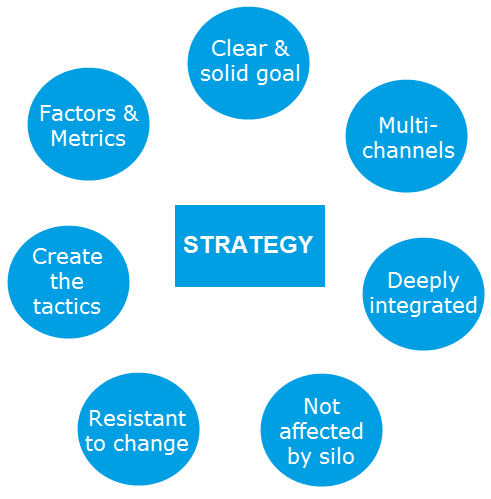
The factors that make up a good strategy
Clear objective: Is the strategy coherent? Ambiguous goals can make your strategy pointless, resulting in tactics being misplaced and leading to failure.
Multi-channel: Do you use multi-channel for your strategy? A good strategy can not be based solely on a distribution channel or advertisement.
Extremely influential: Do the strategies you create have a profound effect on the company’s development? If your strategy does not affect much (which means it’s the same with or without yours), what is the point of building one here?
Unblocked: Is this strategy blocked by internal factors in the company? The key here is the company’s internal problems such as the technical limitations from the product department or the non-cooperation from the Sales department. A good strategy will not let those things affect but actually cover those disadvantages.
Difficult to change: Is this strategy susceptible to change? If the strategy is easy to be manipulated and changed, it is not a good strategy.
Creating tactics: Are the tactics for each of your channels to serve the ultimate strategic goal? It must be based on strategic goals to create tactics, not a set of tactics and then set goals that will be achieved. This is exactly what is said above about tactics that need to be driven.
Factors and indicators: Does your strategy make the connection between the ultimate goal and the success of each tactic? Monitor and evaluate their success factors using KPIs.
After asking yourself the above questions and answering all satisfactorily, you can now carry out your digital marketing strategy.
3 fundamental foundations of digital marketing
There are three fundamental basis that play an integral role in your digital marketing strategy: infrastructure, analytics, and content.
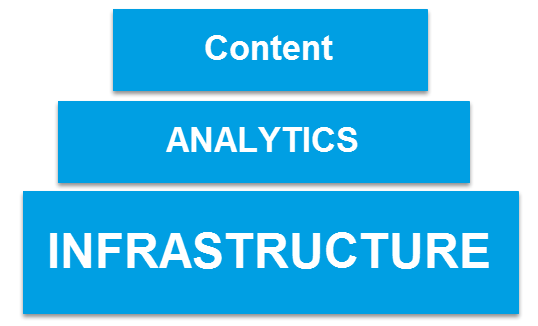
3 fundamental foundations of digital marketing
As you can see in the three elements, the infrastructure plays the most important role (makes it the biggest), then the analysis and finally the content. But don’t think that you can skip any part because all three foundations are crucial to your digital marketing strategy. If not believing, you can try to advertise when your website is down, or do not measure traffic from the channels, or do not have any content on the website.
1. Infrastructure
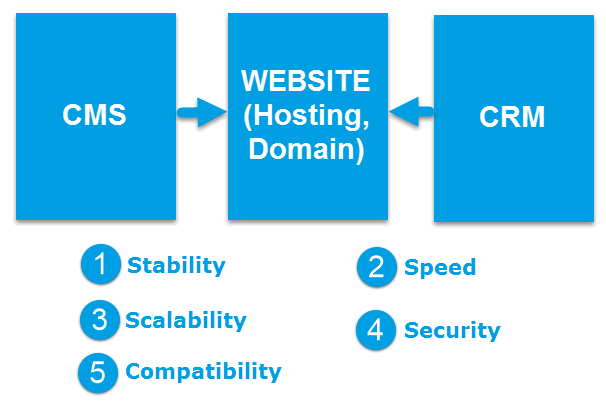
Infrastructure is a paramount factor
Infrastructure in digital marketing is the most essential part of a digital marketing strategy. If this part is not stable then all other factors will go down. Infrastructure include:
– Server, hosting, domain to create a website.
– Database for storing data and customer information. The CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is used to help extracting data from the database easier for marketing, sales, service.
– CMS (Content Management System) is the shirt dressed to help the use, management and posting content on the website becomes easier and faster.
A good infrastructure needs to ensure the following five elements:
Stability: If your website does not work, do not talk about purchasing or anything else, it is not happening. Ensuring a stable 24/7 website is paramount. Or if the website is down, in the fastest way how long it will take to run again?
Speed: Is your website loading fast enough? No one wants to go to a slow website. And the website’s loading speed is associated with your conversion rate: the slower the website loads, the lower the conversion rate and vice versa.
Scalability: What if your website needs to grow from 10,000 to 100,000 visits? If your website can not guarantee the increase in its traffic capacity, you will likely lose a lot of opportunities to be purchased and develop. This is a lesson that we have seen so many times, you run a colon advertising and attract a lot of users but at that time your site crashed, resulting in you not selling anything and losing a number of potential customers because they are frustrated and don’t want to return. Do not repeat this lesson again.
Confidentiality: If your website is hacked and all your customer information is lost then it’s obviously not good for your service at all. If you have a self-build website, make sure you comply with web security standards. If you are using open source CMS such as WordPress, Joomla, Magento, etc., make sure you always update it to the latest edition.
Compatibility: Does your website work well on all browsers, on mobile, on different screen sizes? It’s not possible to test all the cases, but make sure that your site is at least display best on popular browsers and devices.
2. Analytics
Analytics is not just installing Google Analytics into the site and looking at everyday indicators such as sessions, time on site, bounce rate without knowing what to do with it. The analysis here includes measuring the indicators and then finding the direction to improve the desired conversion rate. A visitor goes to your website and then becomes a customer, what happens in the middle? Finding the answer is the work of the analysis. To measure, we usually rely on three major measurement methods:
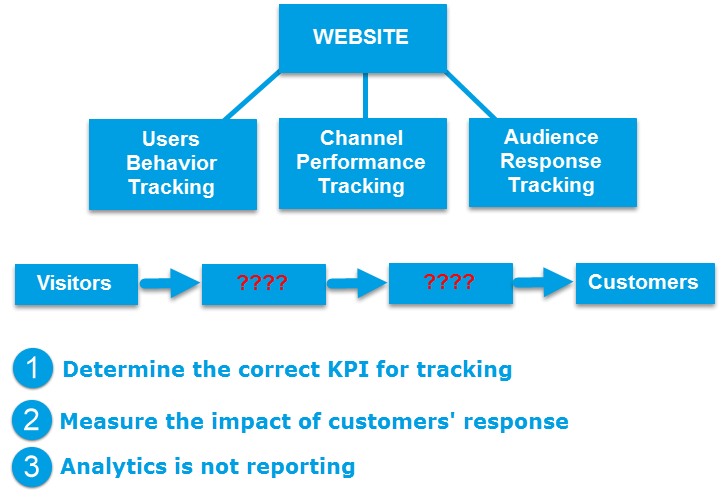
Analysis is finding out what happens when a visitor is converted into a customer
Performance Channel Tracking: Measures the amount of traffic coming from each channel, which channel is performing better, which channel brings more customers, and which channel has the highest number of conversions?
Audience Response Tracking: Measures the user’s response when they are on the site, such as when they are on it, at which page where they left, what pages they view before making the conversion.
User Behavior Tracking: Measures user behavior with tools such as heatmap to find out what do they point on the website, where they click, where scroll to on the page?
There are 3 important things you need to identify with the analysis:
Find the right KPI for tracking: are sessions on the site or followers on the fan page the indicators you want to track? Are they indicators that directly relate to your digital marketing goals? If not then you are wrongly tracking. We will talk more about how to determine the metrics correctly in the section below.
Determine the impact of customer feedbacks: Are customers staying on your site longer than 3 minutes more likely to purchase? Or will customers who visit their company’s website often leave more contact information than those who do not? Understanding the feedback from customers directly impacting the conversion will help you determine which indicators need to be set as KPIs.
Analysis, not report: exporting the data from the measurement tools to excel file and sending it is not analysis, but the report. What you need to know is that from what data you can do?
We will talk about the choice of KPIs for tracking and tracking right below.
See also: Google Analytics and why it is inaccurate
3. Content
Content is everything that you create, it’s not just the text on the website but also the images, infographics, videos or even the company information pages, contact pages, etc. Good content usually satisfies the following five elements:

Content is everything you want to convey to the user
Delivering the content you want to convey to the user who finds you: the first time people visit your website and do not know what your brand is, what they will see and what will remain with them.
Strengthen the content you want to convey to those who already know you: if they ever go to the website and they come in again, your content will help them to remember deeper, more strongly about what you want to convey?
Controlling the communication between the brand and the community, the media: how do you want the social community and people to perceive your brand? Content must make that impression. For example, if your company is a hosting service, people should know about it as a hosting company, not as a website developing company or website design company (even if they are your extra services).
Telling potential customers about your product: If your visitors already have a need, can your content be convincing enough to convert them into customers?
Supporting those who are already a customer: Many businesses are eager to find customers and forget their current customers, while they are potential buyers for upselling and cross-selling. Do you have a FAQ or Knowledge Base page to assist current customers on how to use your product?
Normal content will usually be transmitted through 3 main channels: Owned, Earned, Paid.
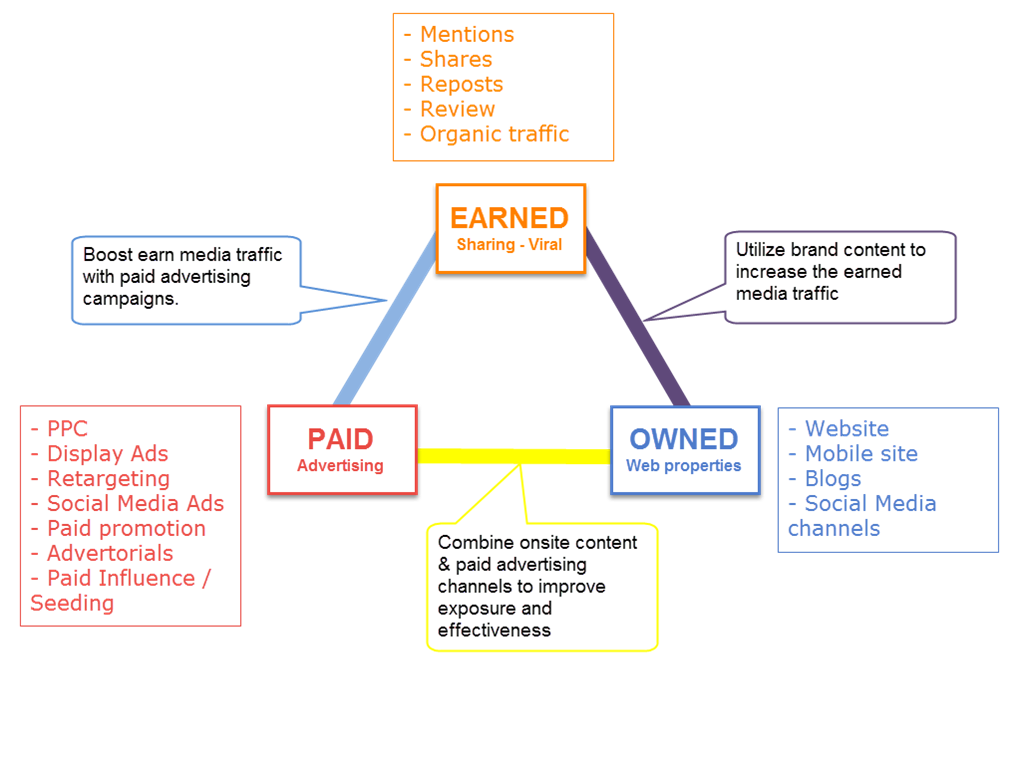
Paid – Owned – Earned are the three main channels used to transmit data
Owned: all channels that you own and have the right to control, publish, edit, delete content including: websites, blogs, social networks, applications.
Earned: These are the channels where your brand is mentioned without any cost, such as social sharing and referrals, reviews, reuploaded contents, or organic traffic.
Paid: The channels that you must pay for your content to appear on it, including: paid search ads, display ads, re-targeting, social ads, seeding, KOL / influencer, etc.
These content delivery channels also have the ability to support each other to increase the likelihood of transmission, for example:
– Share contents from your website or blog to social networks to increase earned traffic (owned – earned).
– Advertise good contents to help them increase coverage and efficiency, such as boosting the posts on Facebook (owned – paid)
– Advertise good contents to increase viral potential and thereby earn more earned media (paid – earned)
3 Steps to Prepare for Planning Your Strategy
In my opinion, that a digital marketing strategy is complete and should be shaped depends considerably on the preparation steps and this is actually the more important part. There are 3 steps you need to do:
1.Assessing the situation
Build a checklist of what you are having by allocating them based on the three core elements outlined above. Here is an example table for you to imagine:
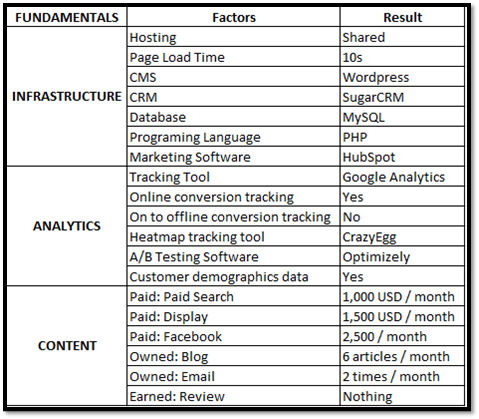
For example, with infrastructure, you need to review what kind of website you are hosting, how long to load the page, what CMS is using, whether CRM is used, what kind of database, the programming language of the website. For the Analytics section you need to determine whether you are using any measurement tools, whether you are tracking online to offline, using heatmap or A / B testing tools, having other demographic data of the customers. For Content, you should check how much you spend on advertising channels, how many blog posts you have, how many emails / sms each month, whether you have a review or PR in the newspaper.
Of course you will need more details and more information. In essence, this is a step where you will need to spend a lot of time gathering information and giving some insights into each of the elements you collect. You will need to evaluate the pros and cons of each of these factors and determine what you can change immediately or where you will need time.
2. Identifying the metrics.
In this step you need to identify which indicators are important to care and use as KPIs. In contrast to popular belief, sessions, bounce rates, time onsite may not be something you should be concerned about. Most people only understand that running ads will generate orders / contracts. But what’s inside is important.
To make it easier to understand, I would use an example of an English language center where the sales process goes from online to offline.
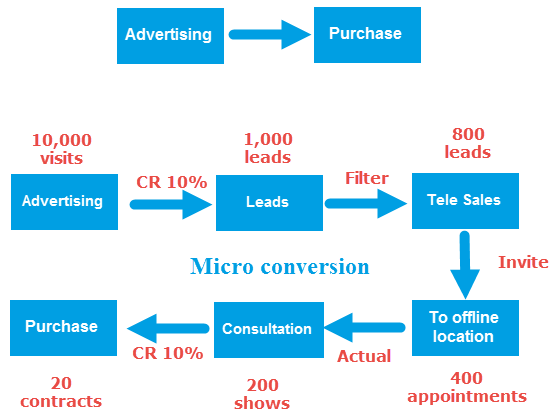
By using ads, I created 10,000 visits / sessions on the website and if 10,000 of those sessions had a conversion rate of 10%, then I had about 1,000 leads. Out of these 1000 leads, after the filter system remove the duplicates or incorrect information, about 800 leads will be qualified and will be called by telesales for further consultation. Approximately 50% of them will agree to set up an appointment, ie 400 appointments to visit the center. Of the 400 dates, there will actually be only 200 people actually show up. Of the 200 people being consulted, if the consultants have the ability to make the sales at 10%, then the center will have 20 contracts.
So from 10,000 traffics, we have created 20 contracts. Each step in this process has a certain conversion rate, and each step directly affects the adjacent steps after it. Each step in this conversion is called a micro conversion. These micro conversions are the KPIs and metrics that you should monitor and evaluate. So, leads, appointments, shows, contracts should be your KPIs, not sessions, bounce rates or time on site.
Knowing the step by step in the process will also help you find out which part has the problem to be able to improve and solve it. For example, if the number of quality leads decreases, then the ad’s settings may not be as good. If the number of appointments decreases, it may be that the telesales call has a problem; or if the conversion rate from the people who show up to the contract is reduced, is the sales team struggling?
Each business will have a different sales process, but it is important that you understand the whole process and the situation at every transition step before you can set up your digital marketing strategy.
3. Setting up a strategic goal
Before moving to setting up a strategic goal, there are some basic definitions that you need to understand:
Average basket size: the average price of the order = the total revenue / number of the order sold. For example, you sell 3 orders, one order costs 50,000 VND, one order is 10,000 VND and the other is 30,000 VND. In total it is 90,000 and divided by 3, the average value of your order is 30,000.
Profit margin: The profit margin is the percentage of the profit divided by the revenue after all other fees have been subtracted. For example, the company’s revenue is 10 billion VND after deducting all office expenses, staff, electricity, water, tax and money.
CAC – Customer Acquisition Cost: For example, you run and ad, which costs 30,000 and you sell 3 orders. CPO (cost per order), the average cost you can sell each order is 10,000 VND. But among 3 orders, one is from a new customer, the other two are from current customers. So the CAC is 30,000 – the amount you have to spend to get a new customer.
CLTV – Customer Life-time Value: How much money customers spend on buying a brand’s product during the whole time of the relationship (between the brand and the customer). For example, one customer purchases once every two months, with an average purchase of 100.000 each time then the customer’s CTLV for a year is 600,000 dong. You can find out more about CLTV in the article on planned obsolescence.
To explain how to set a strategic goal, I would like to use a simple example to make it easier to understand: a production studio, specializing in clothing distribution to Nguyen Trai shops. As a B2B seller, for every garment the shop sells at least 100 items per order. The store is a retailer (B2C) so it can sell one for each purchase.
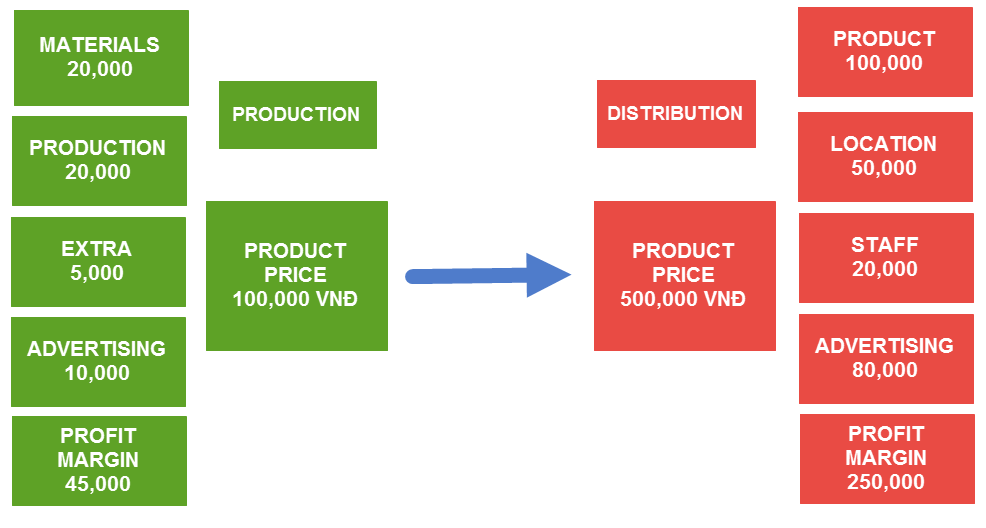
Garment Factory (Production)
The average value of each product sold is 100,000 VND (Average basket size). In which the cost of materials (fabric, knot, button) is 20,000 VND, cost of production (mechanic, electric) is 20,000VND. There are also additional costs (waste, loss) which are 5,000 VND. Finally, the cost of advertising for each shirt is 10,000 VND. In fact, they are a B2B seller so the advertising cost for each order (over 100 shirts) is much higher but eventually it is 10,000 VND for each shirt after dividing. At this point, the profit for every shirt sold after deducting all costs is 45,000 VND, so the profit margin is 45%.
Store (Distribution)
After importing products from the garment factory, they sell at an average price of about 500,000 VND. Of which 100,000 is the cost of importing, then we have the cost of 50,000 VND for location, the cost of staff is 20,000 VND and finally the cost of advertising to sell a shirt is 80,000 VND. At this point the remaining profit is 250,000 VND for each shirt sold and the profit margin is 50%. For the cost of advertising, each 80,000 VND each will generate an order and for every 3 orders, one is sold to a new customer. So the cost to get a new customer (CAC) is 80,000 x 3 = 240,000. At the same time the store also measure that for every customer averagely, once every two months they will return for a purchase, therefore we can calculate how much the average CLTV of the customer is based on the average value they bought .
So, the first important thing for you to determine your strategic goal is to understand your current business situation with such indicators as: Average Basket Size, Profit Margin, CPO, CAC, CLTV as well as actual sales per month. From there you set a standard number that you want to develop to become a strategic target. And from that strategic goal you develop digital marketing strategies and tactics to achieve it.
For example: the garment factory sells 2,000 shirts a month, the monthly revenue is 200 million, the revenue of the year is 2.4 billion and the profit margin is 45%. The garment factory sets a strategic goal of increasing profit margin in the next year to 55% and the revenue just needs to increase to 3 billion. At this point, to maximize the profits, the garment needs to:
– Focus on improving the production process
– Reduce wastage, material loss
– Find fabric supplies at a better cost
– Invest in some types of machines such as button making machine, buttoning machine , printing machine to cut down on outsourcing costs
etc.
If achieved, the profitability of the garment factory next year will be 3 billion x 55% = 1 billion 650 million compared with only 1 billion 80 million in the previous year (up 52%). 52% here is (1650 – 1080) / 1080 = 52%
For the store, if they sell 5,000 shirts a month, the monthly revenue is 2.5 billion, the revenue of the year is 30 billion and the profit margin is 50%. The store sets a strategic goal that the revenue in the next year must increase from 30 billion to 50 billion and they are willing to accept a lower profit margin (40%). To increase the revenue from 30 billion to 50 billion, the store needs to:
– Increase advertising costs (increasing advertising costs sometimes means decreasing effectiveness).
– Start using promotions, discounts to stimulate demand
– Open more stores to reach to more customers
– Start running referral membership programs to improve the CLTV
etc.
If the target is reached, the profit of the store next year will be 50 billion x 40% = 20 billion compared with only 15 billion in the previous year (up 33%).
Through these two examples you can partly understand how to create a strategic goal. Of course, in the process of setting goals, you will need to rely on real-world numbers and indicators and consider various factors, such as inventory, personnel changes, market impact, seasonal changes, the increase of material price, etc.
The numbers you set for your strategic goals must be backed up by market data, tactics with clear KPIs, and the capacity to do so. You can not increase your annual revenue from $ 30 billion to $ 300 billion in a year, or you can not increase the profit margin from 45% to 90%. These are unreal numbers.
Strategic goals are very important, worthy every seconds it takes, but you have to understand it will be the foundation for you to build all the strategies and tactics around it. Do not rush or hurry, take the time to think about it thoroughly.
Building a digital marketing strategy – step by step
Once you have completed the other three steps, you now have enough information, data, and a goal to start building your strategy towards it. During this planning process, it is important to identify what factors affect your overall strategy and which to include in the calculation. You should follow in order the steps listed below to get a complete overall strategy:
1. The master idea
Your business should have a core idea, which can also be understood as the core value or tagline and it symbolizes the brand’s existence and direction. Why is the key idea important and should be addressed when it comes to strategy? Because it has a great influence on what channels you choose and how you can advertise, as well as how to navigate when creating content.
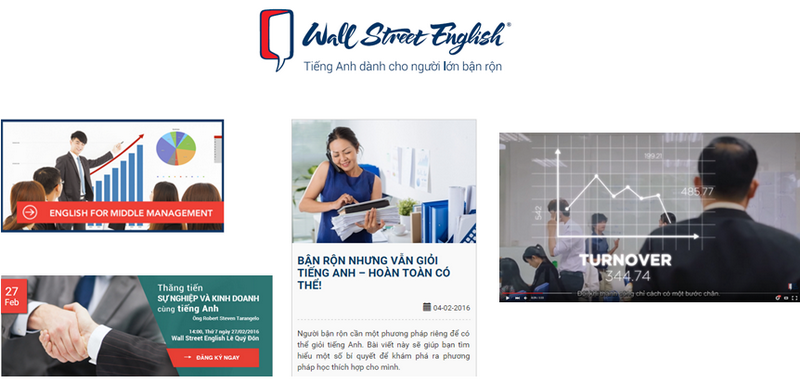
Wall Street English is an example of how content and media focus on the master idea: “English for Busy Entrepreneurs”
2. Estimable Factors

Soucre: freepik
When setting up your digital marketing strategy, you need to figure out all the factors that can affect your strategy’s performance. This includes the estimable factors such as:
– Seasonal effects: depending on the industry, depending on the time of year, there will be different selling possibilities. For example, raincoats will be sold more during the rainy season.
– Trend of the market: What is the current market situation, is it going up or down? Will there be any change in the future?
– Advertising transportation: what if one day Baidu replaces Google and Weibo replaces Facebook in Vietnam?
– The rise of new technologies: What new technologies are going to become popular and how does it affect the advertising channels?
.v.v …
3. Factors that can not be estimated

Source: freepik
Many of you may be wondering: if it can’t be estimated, how can I know to put in the plan? But in essence you still have to cover all the issues such as:
– Communication Crisis: How does it affect the brand and sales?
– Personnel issues: major changes in senior personnel positions.
– One advertising channel disappears: what if Facebook gets blocked in Vietnam?
– Natural disasters: flood, storm, earthquake.
etc.
Think of all the things that can negatively impact your strategy implementation and for each factor, although it may or may not happen, but if it does, what is your backup plan for the situation?
3. Resources: hard and soft costs

Source: freepik
You also need to reconsider your resources.
Hard cost: It’s all you pay with money. This may include the cost of marketing activities, advertising costs, human resources costs for the team members. Generally it includes all kinds of charges that you can measure.
Soft cost: all that can not be paid in money but can be converted into money. This is the part that many people miss while it has a great impact. Your time as well as everyone in your team is an example. If another department ask your designer to help them with a banner and it cost them three hours, it the soft cost. Energy as well as attention is another kind of soft cost that you need to pay attention to.
So every time you calculate the whole and think about the hard cost, you also need to consider whether there are soft costs or other opportunity costs you have to pay, and compare them to the efficiency and results to see if they are worthy . For example, the event you are organizing may cost not only 500 million in organizing expenses but also costs the designer 2 hours a day for design, the executive 4 hours a day to work with the agency, the media officers 1 hour a day to set up your ads, and you a few hours per week for meetings and following up. All that is the opportunity cost that if you do something else, the effect will be better. Therefore you need to consider these factors carefully when planning.
4. Tactics
The tactics discussed above are what we will need to accomplish in order to achieve the strategic goals and the strategic part. For digital marketing the strategy can be viewed as the channels that you will use to convey the master idea mentioned above to potential customers. These will depend on the industry, product or service, each will different tactics. There is no tactical structure suitable for all or you can not take things that your opponent is doing to apply to your business.
Basically, every tactic will need to have a master plan that includes what you will do, the direction, the target audience as well as the number of information and goals you want to achieve for that tactic.
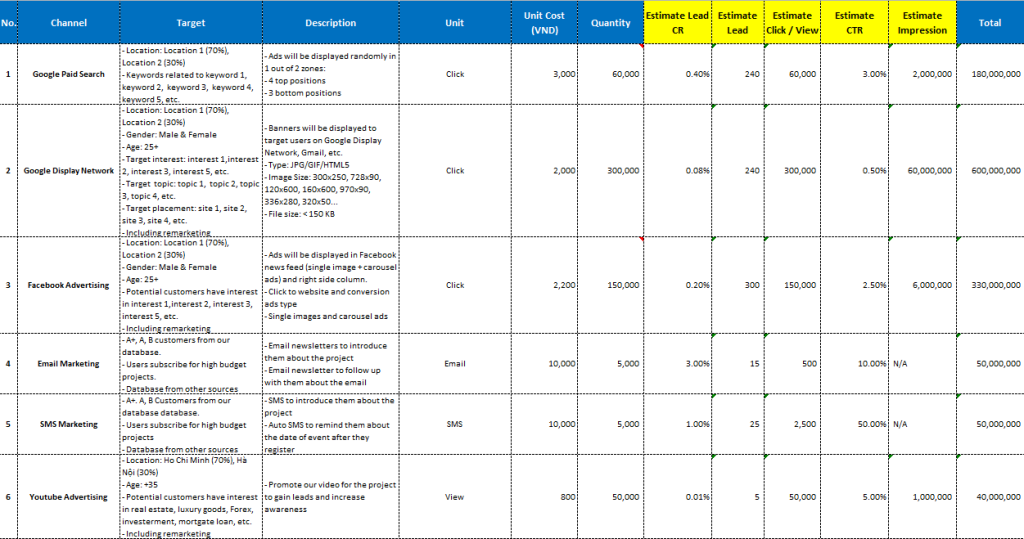
An example on how to set up tatics for channels in digital marketing
You will also need a timeline and a roadmap to accomplish that tactic. You may also need some tools to manage the tasks your team is doing, Slack and Trello are two things I use often.
An example of a timeline for managing tasks
Strategy: easy to say, hard to do but still have to work on
With all of the above things I have discussed, I hope you will have a clearer view of strategy as well as know how to set up a true “true” digital marketing strategy.
I say “yes” and not say good because I think that for strategy and or anything else, you have to have a lot of experience, have to work a lot and have to go through many times to do well. For a person with only 1-2 years of experience, setting up a strategy may be a bit out of the ordinary, but if you need it for the job, hopefully this article will be useful to you and as I say, you just have to do, right or wrong, you will learn more from it.

Source: freepik
And when you have the digital marketing strategy, then you are just done with the easy part. The more difficult part is to implement that strategy, bring all your theories to prove and achieve the ultimate goal. Only by accomplishing it and achieving the goal, you finally can say that your strategy is “good”.
If you have any questions about what I presented, leave a comment below.


 Vietnamese
Vietnamese English
English